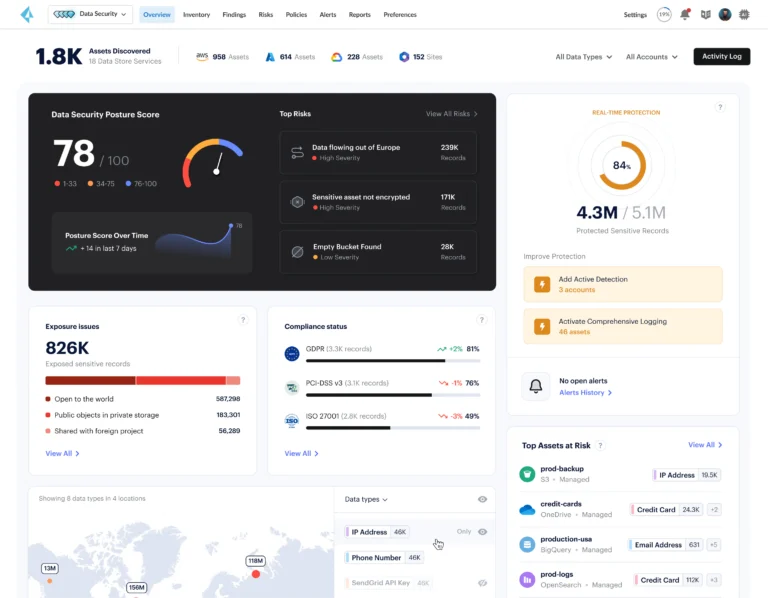
In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, the cybersecurity landscape demands constant innovation. A significant advancement in this field is Extended Detection and Response (XDR). Originating from Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), it marks a critical evolution, offering a holistic, integrated approach to counter modern cyber threats.
What is XDR?
Cybersecurity has evolved to meet the growing complexity of threats. Traditional methods, focusing on isolated defense layers, fall short against coordinated, multivector attacks. This approach addresses this by unifying security data across the entire IT ecosystem – endpoints, networks, cloud, and applications. This integration is key to detecting sophisticated, multistage attacks and reducing response time.
XDR differs significantly from traditional security solutions. It integrates data across multiple sources, offering a broader perspective on threats. This holistic view, combined with automation and real-time monitoring, enables rapid detection and response, outperforming traditional, siloed approaches.
XDR vs. EDR, SIEM, and MDR
- vs. EDR: Extends beyond EDR’s endpoint focus, encompassing multiple vectors for a more integrated approach.
- vs. SIEM: While SIEM systems aggregate and analyze log data, XDR unifies various control points and employs advanced analytics for proactive threat detection.
- vs. MDR: XDR is a security product used by teams, whereas MDR services offer outsourced monitoring and response.
Benefits of Extended Detection and Response
Improved Visibility and Detection Capabilities
key strengths lie in its broad visibility and advanced detection capabilities. It breaks down silos, providing a comprehensive view across all environmental layers. Features like data retention, analysis of internal and external traffic, integrated threat intelligence, and machine learning–based detection are crucial.
Simplified Security Operations
XDR streamlines security operations by consolidating data and automating various tasks. Centralized visibility and predefined playbooks enhance efficiency, allowing security teams to focus on strategic tasks.
Speed of Response and Investigation
It also facilitates rapid triage and investigation of threats. It groups related alerts, offers swift access to forensic artifacts, and provides a consolidated user interface for efficient analysis.
Industry Use Cases of XDR
- Protecting Large Enterprises: Integrated approach is vital for large enterprises, offering comprehensive cybersecurity solutions across various infrastructure components.
- Defending against Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): It’s capabilities are particularly effective against APTs, thanks to its advanced detection and automated response mechanisms.
- XDR for Regulatory Compliance: Assists in meeting various regulatory mandates by providing comprehensive monitoring, threat detection, and documentation capabilities.
Stop attacks with full visibility and analytics with Palo Alto’s Cortex XDR
Implementing Extended Detection and Response: A Strategic Roadmap
The implementation of Extended Detection and Response is a strategic journey that involves multiple steps and considerations. It’s a comprehensive cybersecurity solution, promises enhanced detection, response, and prevention capabilities across various IT environments. This roadmap outlines the key stages and strategies for effectively implementing this in your organization.
1. Assessment and Requirement Analysis
Understanding the Current Landscape
- Evaluate the existing security infrastructure.
- Identify gaps and areas where XDR can bring improvements.
- Assess the types of threats and risks your organization faces.
Defining Goals and Objectives
Establish clear goals for what you want to achieve with XDR (e.g., faster response times, improved detection rates).
Prioritize objectives based on your organization’s specific needs and threat landscape.
2. Building a Knowledge Base
Training and Awareness
- Educate your team about capabilities and benefits.
- Conduct training sessions to build expertise in relevant technologies.
Research and Benchmarking
- Stay informed about the latest trends and developments.
- Benchmark against industry standards and best practices.
3. Vendor Selection and Solution Design
Evaluating Vendors
- Shortlist vendors based on their capabilities, reputation, and alignment with your goals.
- Consider factors such as scalability, integration ease, and support services.
Solution Customization
- Work with the selected vendor to customize the solution to fit your organization’s specific needs.
- Ensure the solution integrates seamlessly with your existing security infrastructure.
4. Integration and Deployment
Integrating Data Sources
- Integrate various data sources like endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and applications.
- Ensure data quality and relevance for effective threat detection.
Phased Deployment
- Implement the XDR solution in phases to manage risks and ensure smooth transition.
- Start with critical areas and gradually expand to other parts of the IT environment.
5. Configuration and Customization
Setting Up Detection and Response Rules
- Configure threat detection rules and response actions tailored to your environment.
- Regularly update these rules based on emerging threats and evolving business needs.
Automating Workflows
- Automate routine tasks for efficiency and faster response.
- Use machine learning and analytics for proactive threat detection and response.
6. Testing and Validation
Conducting Pilot Tests
- Run pilot tests to validate the effectiveness of the solution.
- Use real-world scenarios to assess the system’s detection and response capabilities.
Feedback and Adjustments
- Gather feedback from the security team and end-users.
- Make necessary adjustments to optimize performance and usability.
7. Ongoing Training and Skill Development
Continuous Learning
- Encourage continuous learning and skill development among your security team.
- Keep abreast of new features and functionalities.
Cross-Functional Training
- Train other IT and relevant staff to ensure they understand the role of XDR in the broader security context.
8. Performance Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Monitoring Key Metrics
- Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like detection time, response time, and false positive rates.
- Regularly review these metrics to assess the effectiveness of the XDR solution.
Regular Assessments and Updates
- Conduct periodic security assessments to identify areas for improvement.
- Update and refine the XDR solution based on these assessments and evolving threat landscapes.
9. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Ensuring Compliance
- Align the implementation with relevant regulatory requirements and standards.
- Use reporting capabilities for compliance documentation and audits.
10. Vendor Collaboration and Support
Maintaining Vendor Relationships
- Keep a collaborative relationship with the vendor for ongoing support and updates.
- Leverage vendor expertise for troubleshooting and advanced threat analysis.